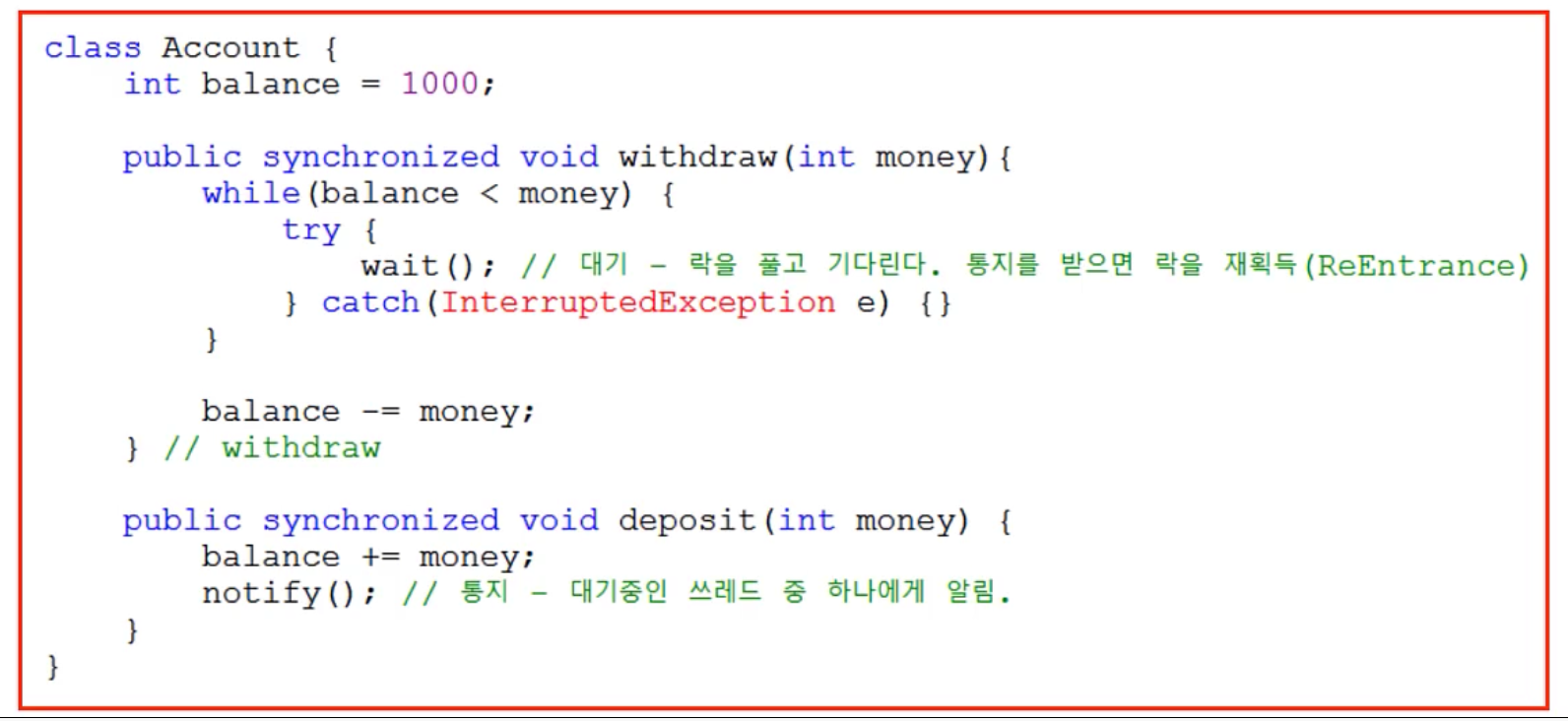
Java wait()과 notify()
by 볼빵빵오춘기wait()과 notify()
- 동기화의 효율을 높이기 위해 wait(), notify()를 사용한다.
- wait() - 기다리기, notify() - 통보하기
- Object클래스에 정의되어 있으며, 동기화 블록 내에서만 사용할 수 있다.
- wait() : 객체의 lock을 풀고 스레드를 해당 객체의 waiting pool에 넣는다.
- notify() : waiting pool에서 대기중인 쓰레드 중의 하나를 깨운다.
- nofifyAll() : waiting pool에서 대기중인 모든 쓰레드를 꺠운다.
예제
아래 상황을 두고
- 요리사는 Table에 음식을 추가하면 손님은 Table의 음식을 소비한다.
- 요리사와 손임이 같은 객체(Table)을 공유하므로 동기화가 필요하다.
예제1 - 동기화x 일 때
더보기
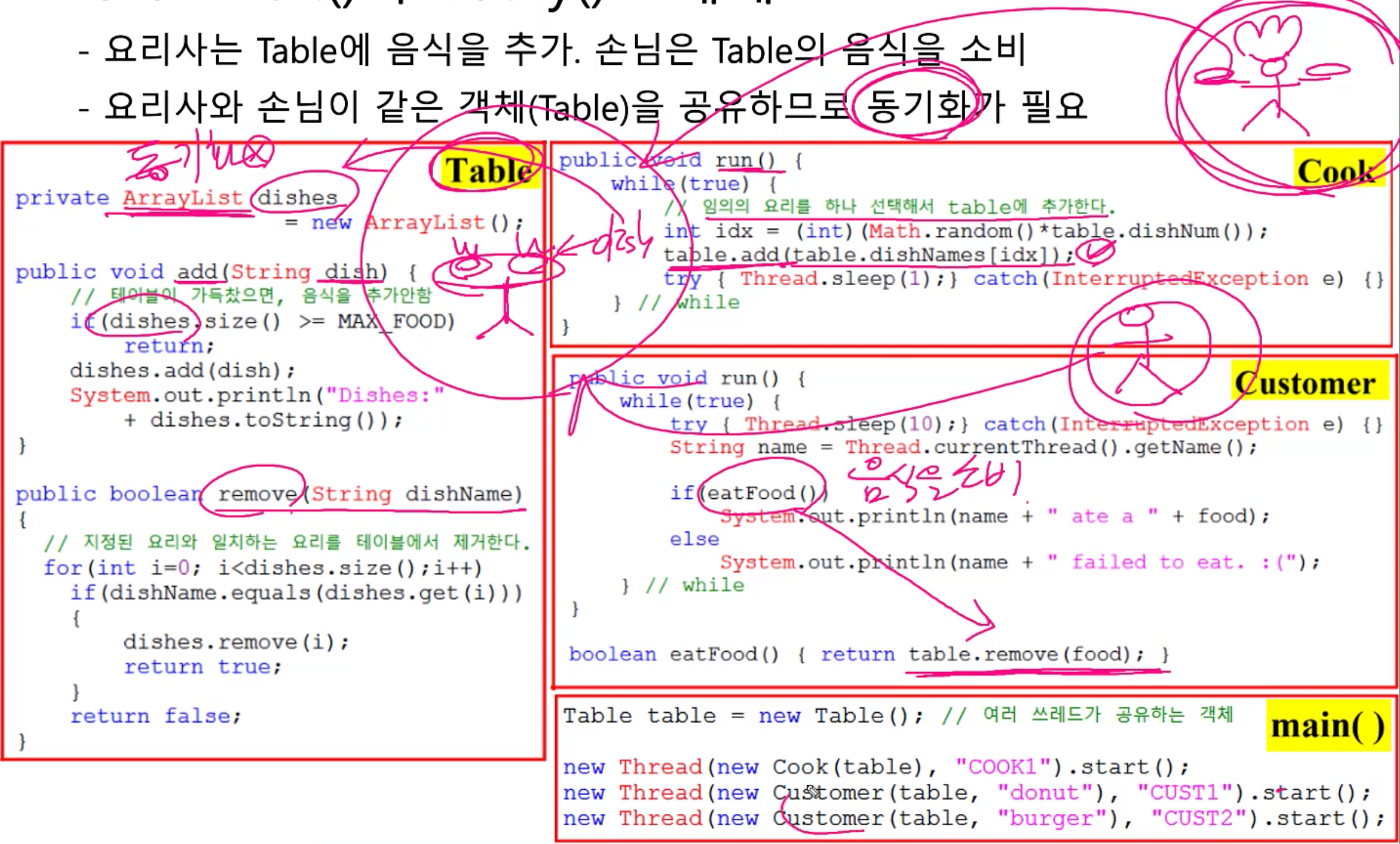

⇒ 요리사는 table에 음식(dish)을 추가하는 일을 한다.
⇒ 손님은 table의 음식(dish)을 먹는 일을 한다.

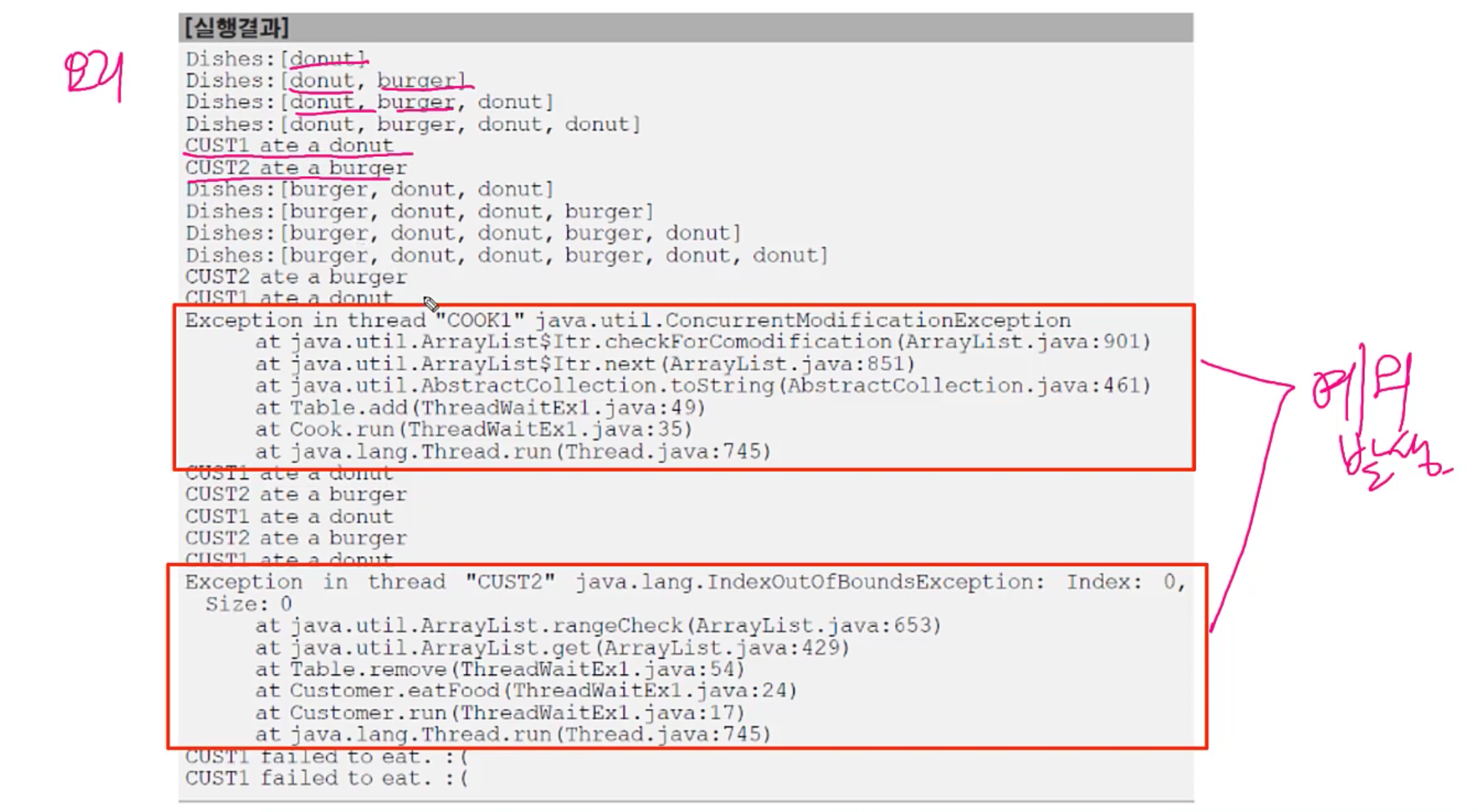
결과
⇒ 에러뜬다. 예외발생한다. 항상 예외가 나는것은아니지만 돌리다보면 에러가 난다.
⇒ [예외1] 요리사가 Table에 요리를 추가하는 과정에 손님이 요리를 먹는다.
⇒ [예외2] 하나 남은 요리를 손님2가 먹으려하는데, 손님1이 먹는다.
why? Table을 여러 쓰레드가 공유하기 때문에 작업 중에 끼어들기 발생한다.
예제2 - 동기화o
더보기
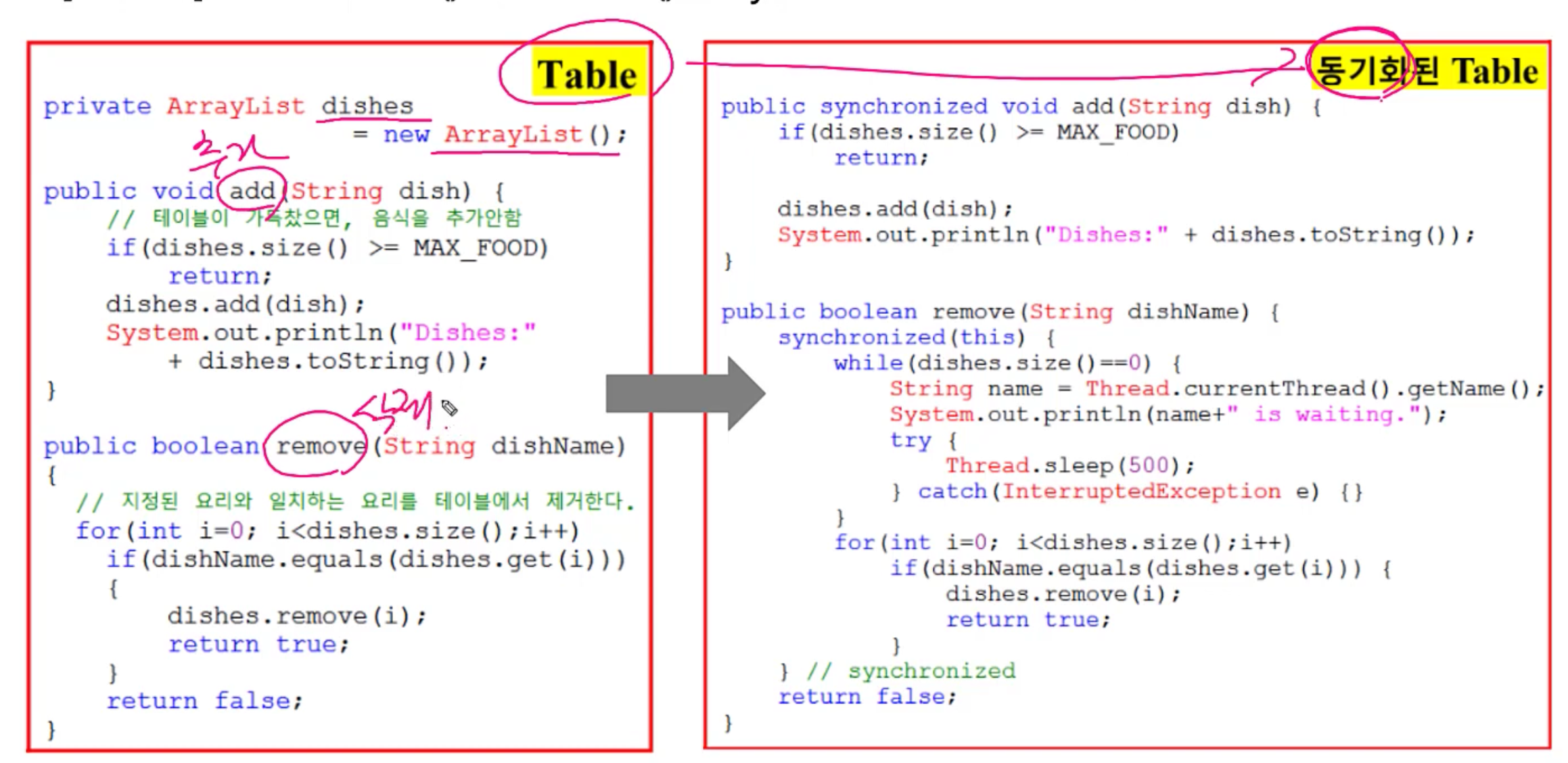

[1번의 문제점] Table을 여러 쓰레드가 공유하기 때문에 작업 중에 끼어들기 발생했다.
[해결책] Table의 add()와 remove()를 synchronized로 동기화


결과
예외는 발생하지 않지만, 손님(CUST2)이 Table에 lock건 상태를 지속 요리사가 Table의 lock을 얻을 수 없어서 음식을 추가하지 못 한다.
더보기
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Customer implements Runnable {
private Table table;
private String food;
Customer(Table table, String food) {
this.table = table;
this.food = food;
}
public void run() {
while(true) {
try { Thread.sleep(10);} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(eatFood())
System.out.println(name + " ate a " + food);
else
System.out.println(name + " failed to eat. :(");
} // while
}
boolean eatFood() { return table.remove(food); }
}
class Cook implements Runnable {
private Table table;
Cook(Table table) { this.table = table; }
public void run() {
while(true) {
int idx = (int)(Math.random()*table.dishNum());
table.add(table.dishNames[idx]);
try { Thread.sleep(100);} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
} // while
}
}
class Table {
String[] dishNames = { "donut","donut","burger" };
final int MAX_FOOD = 6;
private ArrayList<String> dishes = new ArrayList<>();
public synchronized void add(String dish) { // synchronized를 추가
if(dishes.size() >= MAX_FOOD)
return;
dishes.add(dish);
System.out.println("Dishes:" + dishes.toString());
}
public boolean remove(String dishName) {
synchronized(this) {
while(dishes.size()==0) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name+" is waiting.");
try { Thread.sleep(500);} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
}
for(int i=0; i<dishes.size();i++)
if(dishName.equals(dishes.get(i))) {
dishes.remove(i);
return true;
}
} // synchronized
return false;
}
public int dishNum() { return dishNames.length; }
}
class Ex13_14 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Table table = new Table(); // 여러 쓰레드가 공유하는 객체
new Thread(new Cook(table), "COOK").start();
new Thread(new Customer(table, "donut"), "CUST1").start();
new Thread(new Customer(table, "burger"), "CUST2").start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.exit(0);
}
}예제3 - 해결
더보기
[문제점]
음식이 없을 때, 손님이 Table의 lock을 쥐고 안놓는다.
요리사가 lock을 얻지 못해서 Table에 음식을 추가할 수 없다.
[해결책]
음식이 없을 때, wait()으로 손님이 lock을 풀고 기다리게 하자.
요리사가 음식을 추가하면, notify()로 손님에게 알리자.(손님이 lock을 재획득)

⇒ 손님은 음식이 없으면 대기(wait())하고, 음식을 먹고나면 요리사에게 통보(notify())한다.
⇒ 전과 달리 한 쓰레드가 lock을 오래 쥐는 일이 없어지며 효율적이게 된다.
더보기
import java.util.ArrayList;
class Customer2 implements Runnable {
private Table2 table;
private String food;
Customer2(Table2 table, String food) {
this.table = table;
this.food = food;
}
public void run() {
while(true) {
try { Thread.sleep(100);} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
table.remove(food);
System.out.println(name + " ate a " + food);
} // while
}
}
class Cook2 implements Runnable {
private Table2 table;
Cook2(Table2 table) { this.table = table; }
public void run() {
while(true) {
int idx = (int)(Math.random()*table.dishNum());
table.add(table.dishNames[idx]);
try { Thread.sleep(10);} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
} // while
}
}
class Table2 {
String[] dishNames = { "donut","donut","burger" }; // donut의 확률을 높인다.
final int MAX_FOOD = 6;
private ArrayList<String> dishes = new ArrayList<>();
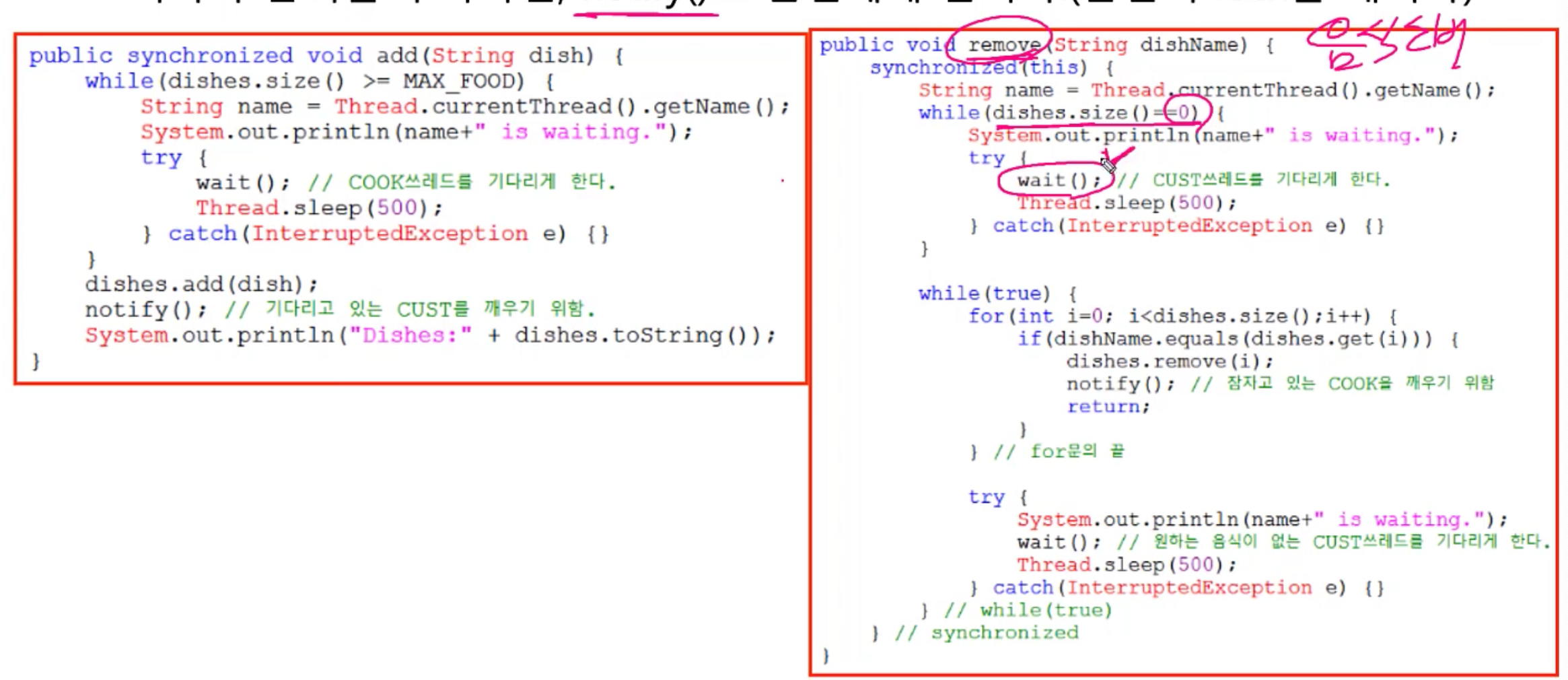
public synchronized void add(String dish) {
while(dishes.size() >= MAX_FOOD) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name+" is waiting.");
try {
wait(); // COOK쓰레드를 기다리게 한다.
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
}
dishes.add(dish);
notify(); // 기다리고 있는 CUST를 깨우기 위함.
System.out.println("Dishes:" + dishes.toString());
}
public void remove(String dishName) {
synchronized(this) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
while(dishes.size()==0) {
System.out.println(name+" is waiting.");
try {
wait(); // CUST쓰레드를 기다리게 한다.
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
}
while(true) {
for(int i=0; i<dishes.size();i++) {
if(dishName.equals(dishes.get(i))) {
dishes.remove(i);
notify(); // 잠자고 있는 COOK을 깨우기 위함
return;
}
} // for문의 끝
try {
System.out.println(name+" is waiting.");
wait(); // 원하는 음식이 없는 CUST쓰레드를 기다리게 한다.
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
} // while(true)
} // synchronized
}
public int dishNum() { return dishNames.length; }
}
class Ex13_15 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Table2 table = new Table2();
new Thread(new Cook2(table), "COOK").start();
new Thread(new Customer2(table, "donut"), "CUST1").start();
new Thread(new Customer2(table, "burger"), "CUST2").start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.exit(0);
}
}'👩🏻💻 About 프로그래밍 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java 함수형 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.12.11 |
|---|---|
| Java 람다식(Lambda Expression) (0) | 2023.12.11 |
| Java 쓰레드의 동기화(synchronization) (1) | 2023.12.09 |
| Java 쓰레드의 실행제어 메서드 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
| Java 데몬쓰레드(deomon thread), 쓰레드의 상태 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
블로그의 정보
Hello 춘기's world
볼빵빵오춘기